WeChat QR Code scanner is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based library to detect and decode QR codes. As the name suggests, it was developed and contributed by the WeChat Computer Vision team. It was integrated into OpenCV with the release 4.5.2 in the opencv-contrib package.
In this blog post, we will go through python and c++ code for implementing the WeChat QR code scanner in OpenCV and compare its performance with the built-in QR code scanner of OpenCV.
1. Structure of a QR code
At the very outset, let us take a look at the structure to get a basic idea of QR code formatting.
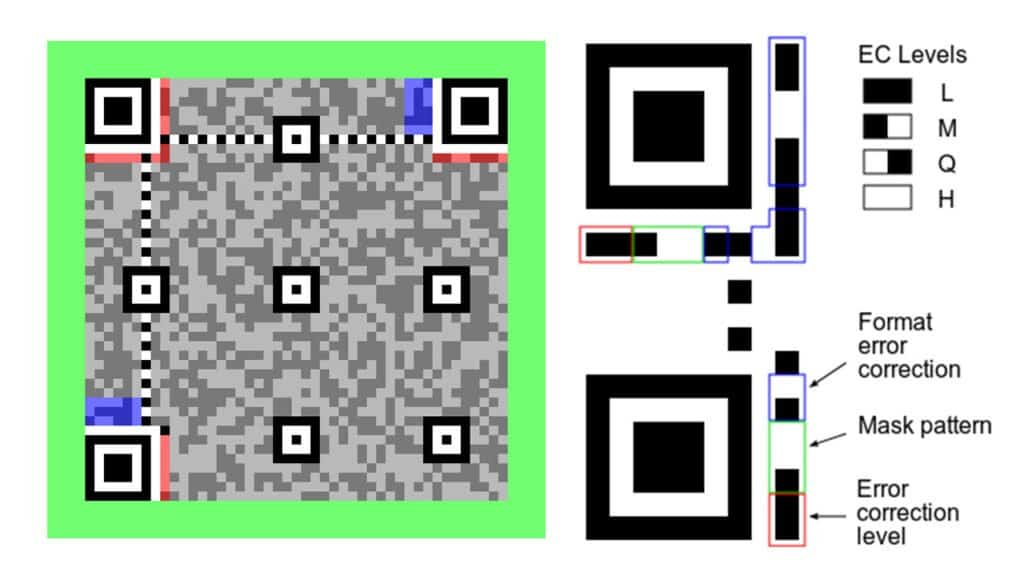
fig: Structure of a QR code. source: Wikipedia
The illustration shows the format parameters of a QR code. Five parameters describe the format of a QR code to the decoder.
- Position
- Timing
- Error correction level
- Mask pattern
- Format error correction
The distinct black squares containing smaller squares are the tracker boxes that help determine the position and rotation of the QR code. The timing (repeating black and white pattern between position boxes) provides information about the size of the QR code. There are 40 different types of QR code based on the timing.
Version 1 ( 21×21 box), Version 2 (25×25), version 3(29×29) to version 40 (177×177). Error correction level tells about the percentage of data bytes that can be recovered. Based on the level of error correction, there can be 4 different categories. Low(7%), medium(15%), quartile(25%) and high(30%). The higher the level, the lower is the storage capacity. The scanner detects the QR code with the help of these parameters and decodes the data. In this blog post, we are not going to discuss every parameter in detail. If you are interested in knowing how a QR code is encoded and decoded, check out this link for more information. Moreover, there are plenty of good online resources explaining QR code.
2. WeChat QR Code Scanner in OpenCV
The WeChat QR code scanner is part of the opencv-contrib repository.
Please download the code from the link above. Navigate to the code folder, fire up terminal/powershell and install the required packages using the requirements.txt file. Now, without further ado, let’s dive into the code.
pip install -r requirements.txt
3. Python Code Implementing Wechat QR Code in OpenCV
3.1 Import Libraries
import cv2
import sys
import time
3.2 Function to generate a bounding box
The bounding box coordinates are obtained from the detector as a list. Hence, we convert them to tuples for drawing lines.
def displayBbox(im, bbox):
if bbox is not None:
bbox = [bbox[0].astype(int)]
n = len(bbox[0])
for i in range(n):
cv2.line(im, tuple(bbox[0][i]), tuple(bbox[0][(i+1) % n]), (0,255,0), 3)
3.3 Instantiate WeChat QR Code detector
WeChat QR code scanner uses two CNN models internally.
- Detector Model: This CNN model is used to locate the QR code.
- Super Resolution Model: The class of techniques used for improving the resolution of an image is called Super Resolution. WeChat QR code scanner uses a super-resolution model to enhance the resolution of the QR code. It is, therefore, able to deliver superior results when the resolution of the QR code is small (e.g., when you are scanning it from far away.)
The two CNN models are in the Caffe Deep Learning framework format which consists of two files-
- A model architecture file (“model.prototxt”)
- A model weights file (“model.caffemodel”) contains the weights and biases learned in the training process.
We have included these files in the model directory. You can also download these files from this link.
The default OpenCV detector uses traditional computer vision methods for detection and decoding.
3.4 Main Function
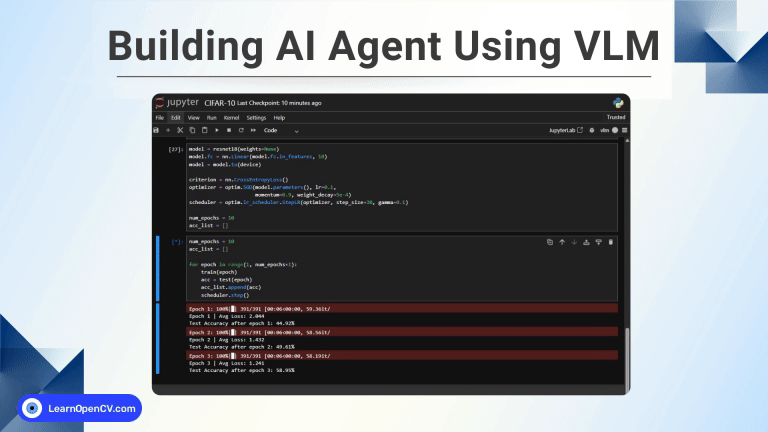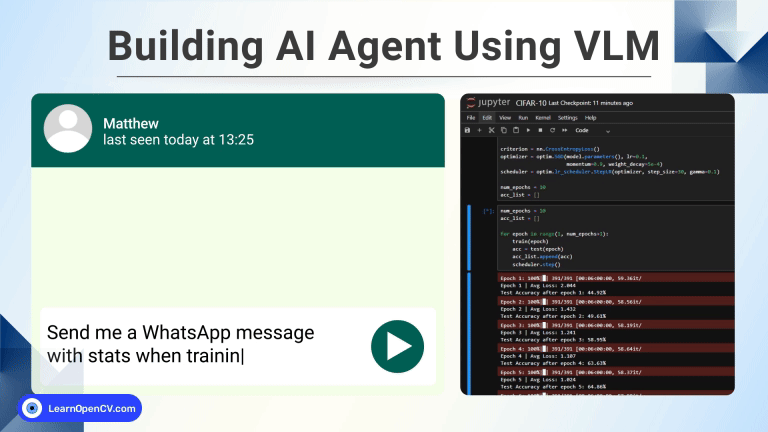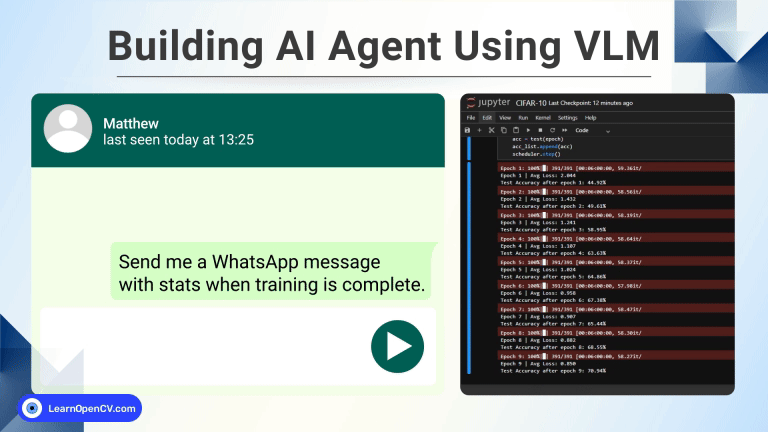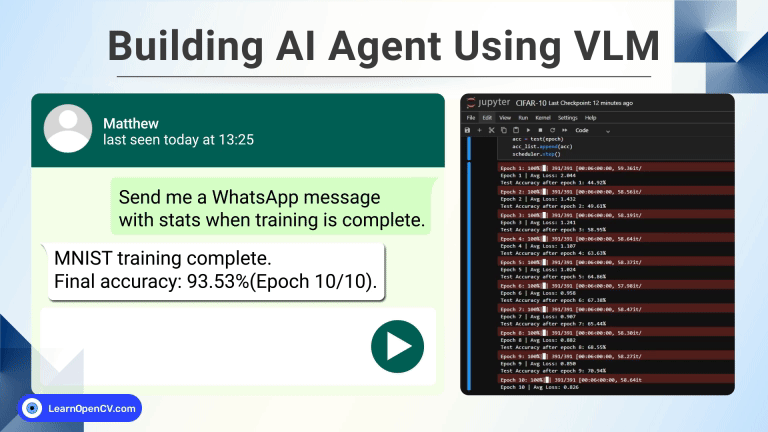
In the main function, we first read the image. Then use the detectAndDecode method to parse the QR code. You can also pass your QR code image in the command line. We calculate the time of execution using the time module and obtain the output in milliseconds.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Load image.
if len(sys.argv)>1:
img = cv2.imread(sys.argv[1])
else:
img = cv2.imread('sample-qrcode.jpg')
t1 = time.time()
# Detect and decode.
res, points = detector.detectAndDecode(img)
t2 = time.time()
# Detected outputs.
if len(res) > 0:
print('Time Taken : ', round(1000*(t2 - t1),1), ' ms')
print('Output : ', res[0])
print('Bounding Box : ', points)
displayBbox(img, points)
else:
print('QRCode not detected')
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
4. C++ Code Implementing Wechat QR Code in OpenCV
The CMakeLists.txt file has been provided within the downloaded code.
4.1 Include Libraries
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/wechat_qrcode.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace std::chrono;
4.2 Utility function to draw a bounding box
The detect and decode method in c++ returns a vector containing the bounding box coordinates. Which is converted to Mat so as to access the elements as shown below.
void display(Mat &im, Mat &bbox)
{
int n = bbox.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
line(im, Point2i(bbox.at<float>(i,0), bbox.at<float>(i,1)),
Point2i( bbox.at<float>((i+1) % n,0),
bbox.at<float>((i+1) % n,1)), Scalar(0,255,0), 3);
}
imshow("Image", im);
}
4.3 Main Function
Similar to python, we read the image from command line input or use the default image. The output data and bounding box coordinates are stored in string res and vector points respectively. Unlike python, here we need to take care of the data type.
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Instantiate WeChat QR Code detector.
Ptr<wechat_qrcode::WeChatQRCode> detector;
detector = makePtr<wechat_qrcode::WeChatQRCode>(
"../model/detect.prototxt",
"../model/detect.caffemodel",
"../model/sr.prototxt",
"../model/sr.caffemodel");
// Read image from command line input or the default.
Mat img;
if(argc>1)
{
img = imread(argv[1]);
}
else
img = imread("sample-qr-code.jpg");
// Declare vector 'points' to store bounding box coordinates.
vector<Mat> points;
// Start time.
auto start = high_resolution_clock::now();
// Detect and decode.
auto res = detector->detectAndDecode(img, points);
// End time.
auto stop = high_resolution_clock::now();
// Time taken in milliseconds.
auto duration = duration_cast<milliseconds>(stop - start);
// If detected.
if (res.size() > 0)
{
// Print detected data.
for (const auto& value : res)
{
cout << value << endl;
}
// Iterate through the vector and convert to Mat. Required,
// as we need to access the elements while drawing the box.
Mat1f matBbox;
for(int i=0; i<points[0].size().height; i++)
{
matBbox.push_back( points[0].row(i));
}
cout << "Time taken : " << duration.count() <<
" milliseconds" << endl;
cout << matBbox << endl;
// Display bounding box.
display(img, matBbox);
}
else
cout << "QR Code not detected." << endl;
imshow("Image", img);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
4.4 WeChat QR Code OpenCV Output
The decoded data is shown in the terminal along with the execution time and a bounding box is drawn around the detected QR Code.
http://LearnOpenCV.com
Time taken : 18 milliseconds
[242.27815, 62.109261;
402.75635, 62.109261;
402.75635, 225.11674;
242.27815, 225.11674]

5. OpenCV vs WeChat QRCode
We took 4 QR code samples in increasing order of complexity as shown below and performed analysis on the following grounds. We are going to plot the processing time using bar graphs and create a table for the rest of the qualitative variations.
- Processing time.
- Occluded image (less than 15% of the QR code)
- Low light situation
- Far away images ( 1.5-2.0 meters, resolution : 640x480p)
- Blurred images ( Gaussian Blur, various kernel sizes)
- Rotated images

fig: QR code samples
Sample 1
- Encoded data: [https://learnopencv.com]
- Type: Version 2 (25×25)
- Error level: Quartile (25%)
- Time taken by OpenCV: 17.02 ms
- Time taken by WeChat: 24.72 ms
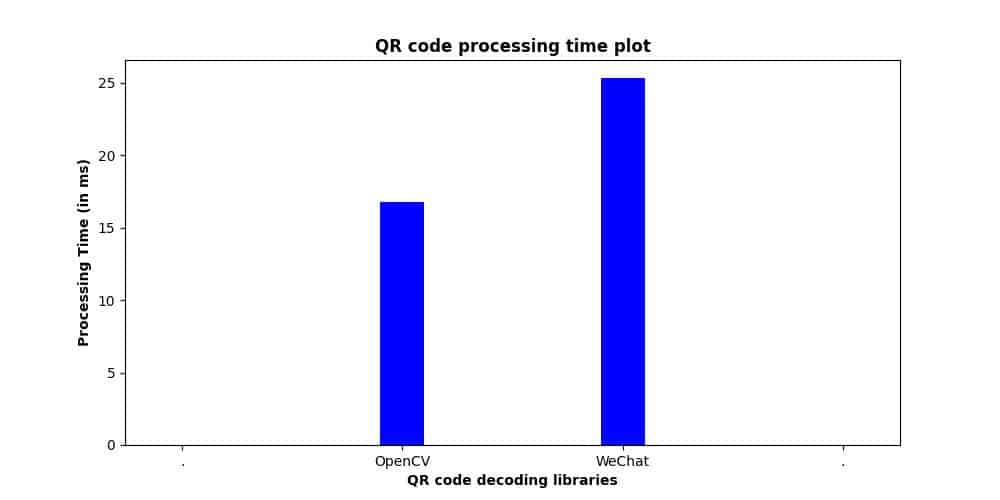
fig: QR code parsing time plot for sample 1
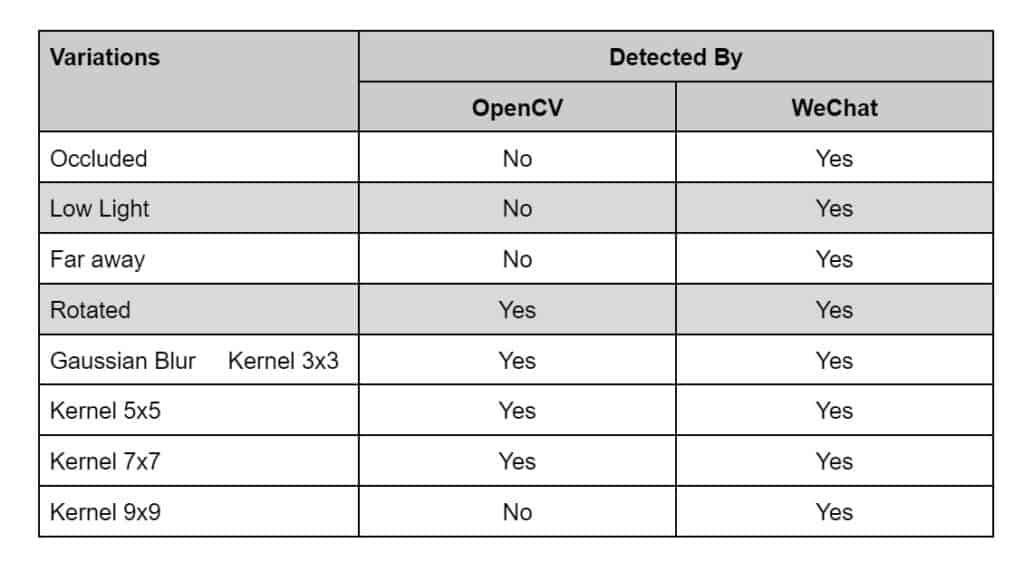
Table 1: Observations on sample 1

fig: Occluded QR code

fig: Low light condition

fig: Far away

fig: Rotated

fig: Gaussian Blurred (kernel size 3, 5, 7, and 9 respectively)
Sample 2
- Encoded Data: [Why is 11 not pronounced as ‘onety one’?]
- Type: Version 3 (29×29)
- Error level: Quartile (25%)
- Time taken by OpenCV: 18.82 ms
- Time taken by WeChat: 23.77 ms
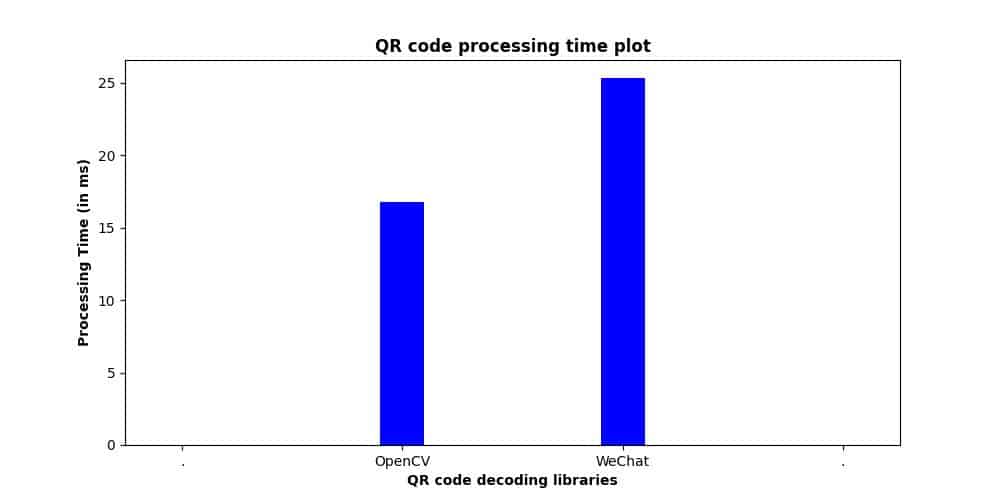
fig: QR code parsing time plot for sample 2
The observations on sample 2 are similar to sample 1 except for the blurred images.

fig: Gaussian Blurred (kernel size 3, 5, 7 and 9 respectively)
Sample 3
- Encoded Data: [Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat]
- Type: Version 9 (53×53)
- Error level: Quartile (25%)
- Time taken by OpenCV: 426.8 ms
- Time taken by WeChat: 26.0 ms
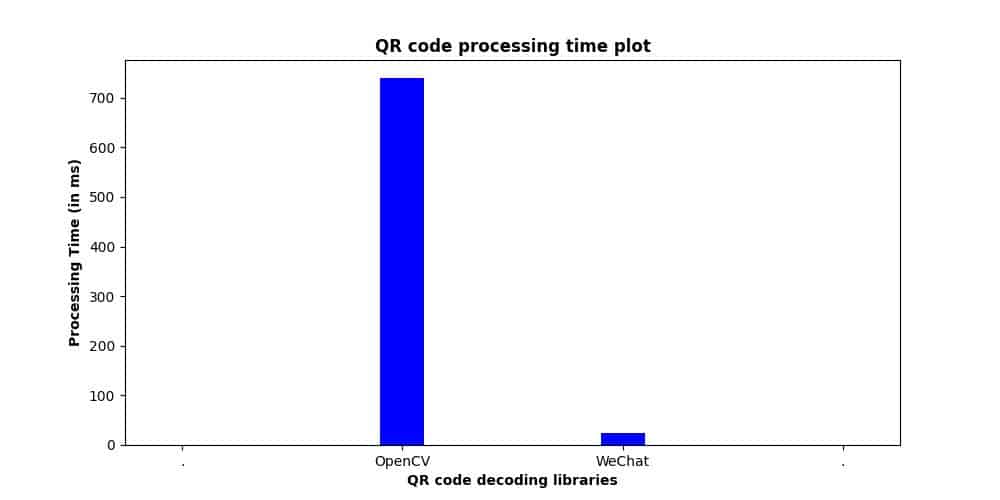
fig: QR code parsing time plot for sample 3
For the last two samples, OpenCV was performing marginally better than WeChat but when we increased the complexity of the QR code, WeChat outperformed OpenCV.
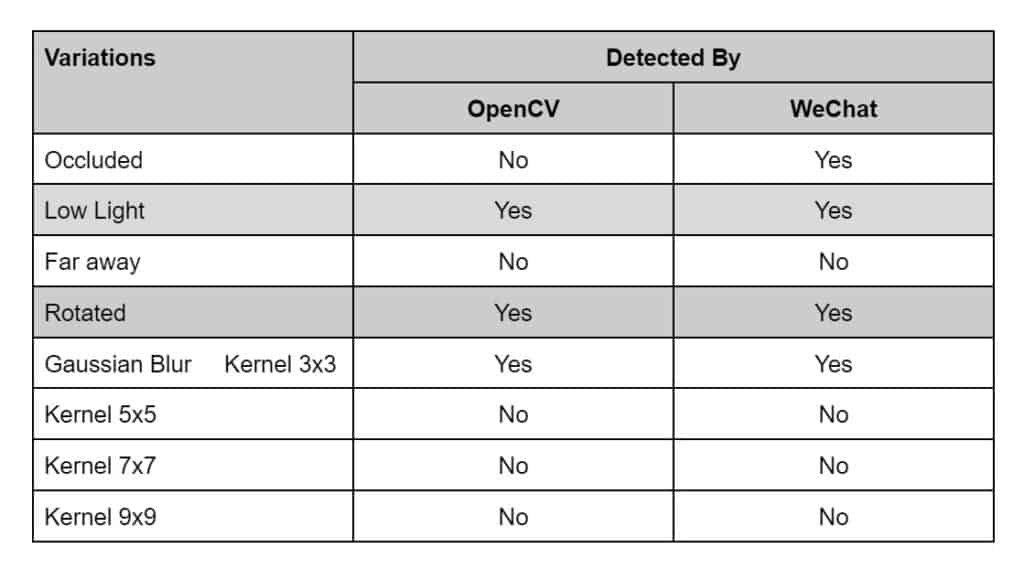
Table 2: Observations on sample 3

fig: Occluded QR code

fig: Low light condition

fig: Far away

fig: Rotated

fig: Gaussian Blurred (kernel size 3, 5, 7 and 9 respectively)
Sample 4
- Encoded Data: [1. 70% of the earth’s surface is covered in water. However, only 3% of the earth’s water is freshwater and two-thirds of the freshwater is frozen in ice sheets and glaciers. The other third is found in lakes, rivers, and underground. \n2. Back in a jiffy? You’d better be fast! A “jiffy” is an actual length of time, equal to about 1/100th of a second]
- Type: Version 12 (65×65)
- Error level: Quartile (25%)
- Time taken by OpenCV: Failed to parse.
- Time taken by WeChat: 30.5 ms
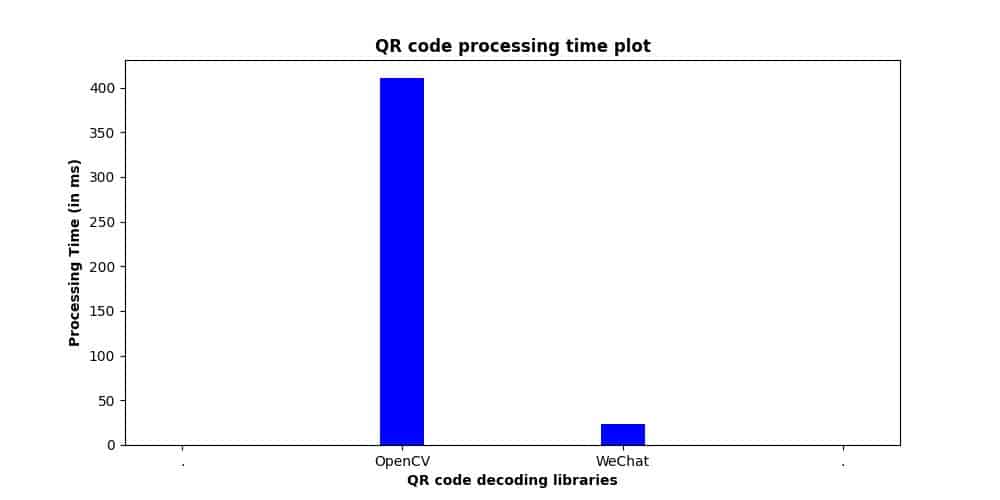
fig: QR code parsing time plot for sample 4
Here, OpenCV failed to decode the QR code after processing for about 730 ms. Whereas WeChat completed processing in just 30.5 ms. The observations, in this case, are similar to sample 3, except for the OpenCV QR code decoder.

fig: Gaussian Blurred (kernel size 3, 5, 7 and 9 respectively)
WeChat QR Code Scanner Conclusion
From the experiment above, we observed that OpenCV performs fairly well for QR code with lesser information. However, it performs poorly on complex QR code and mostly fails above a certain complexity. From the video, we can see that OpenCV has a better corner detection algorithm but that does not necessarily imply better decoding. WeChat is more robust to variations like rotation or when it’s far away. All in all, if you are building an application that requires parsing of complex QR code and time is a concern, then WeChat is the choice. Otherwise, the OpenCV QR code decoder works fine.
So that’s all about the experiment that we performed on OpenCV and WeChat QR code decoder. I hope you enjoyed reading the post and learned a few things. If you are interested in learning about a library even better than both OpenCV and WeChat, check out our previous post on zBar.



100K+ Learners
Join Free OpenCV Bootcamp3 Hours of Learning