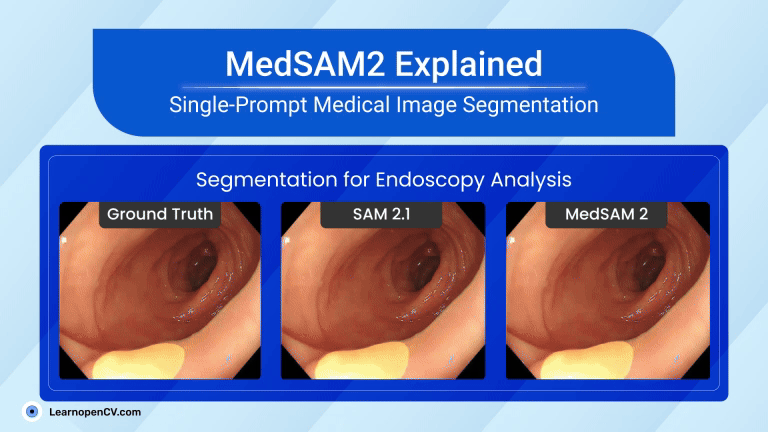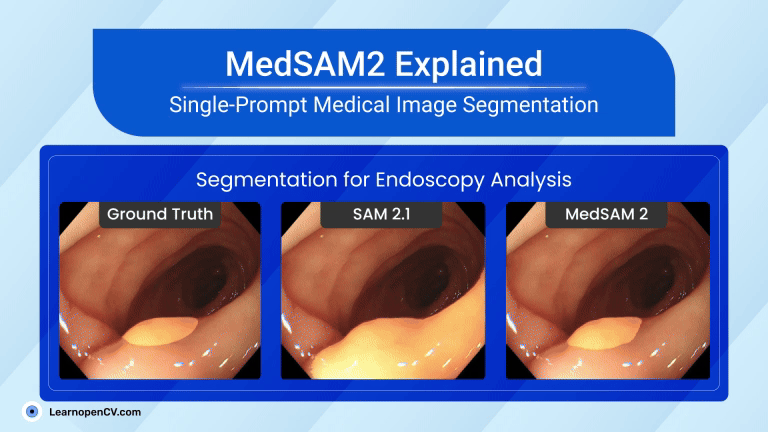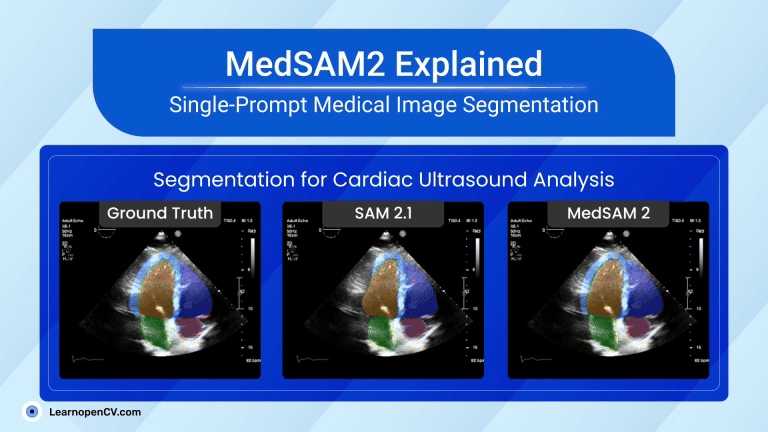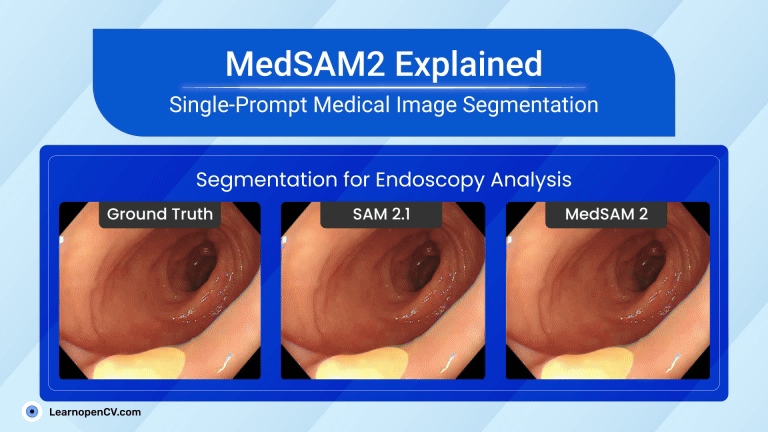
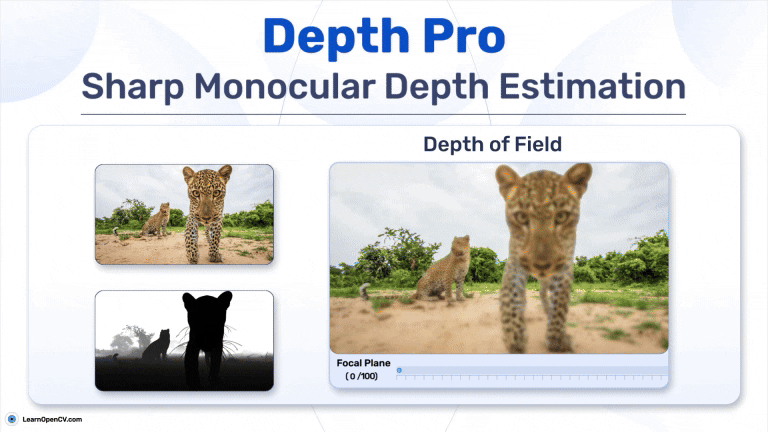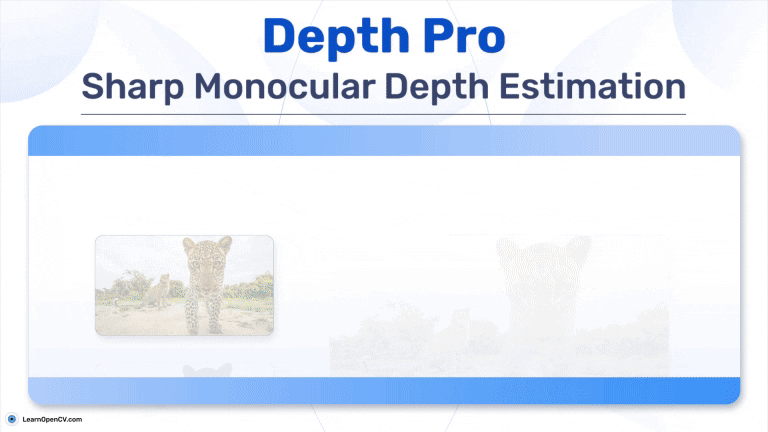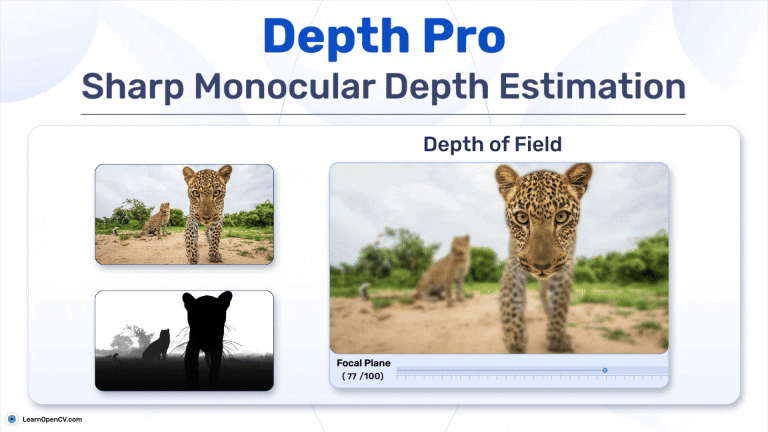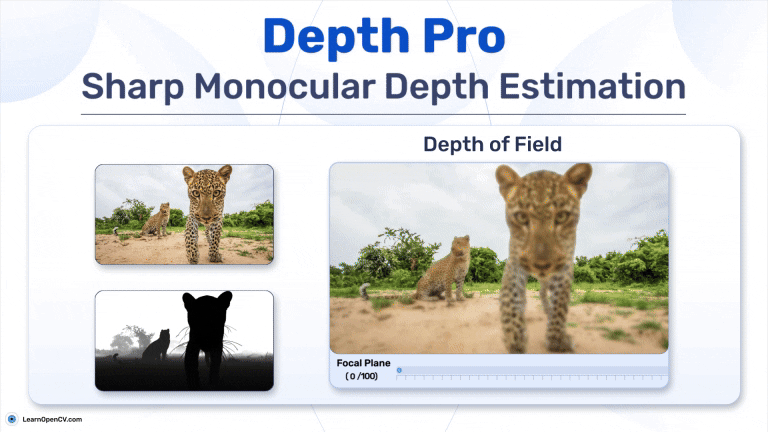
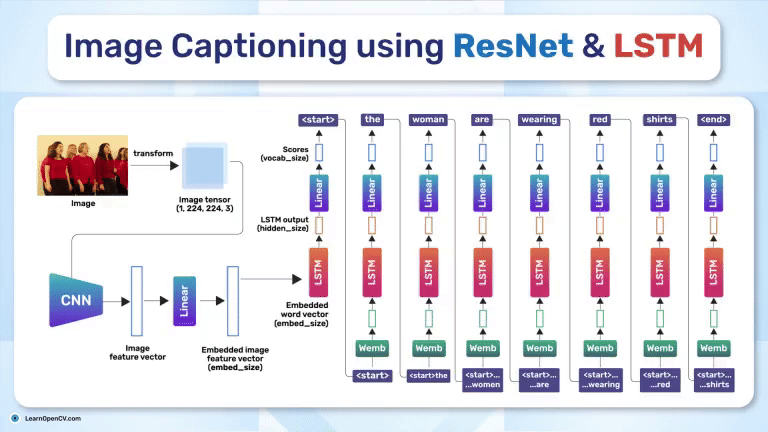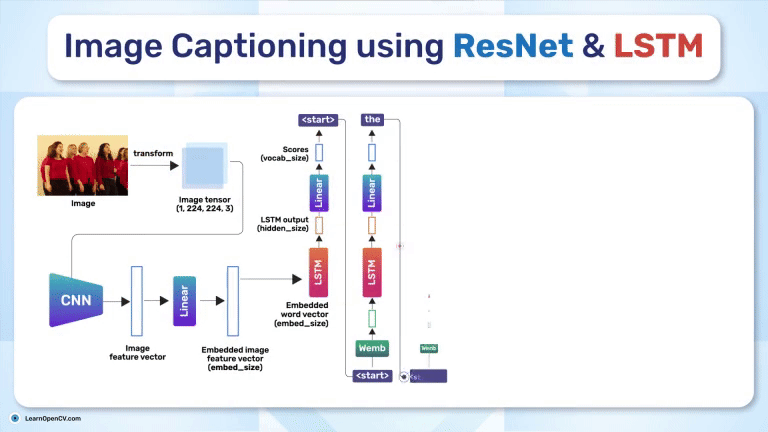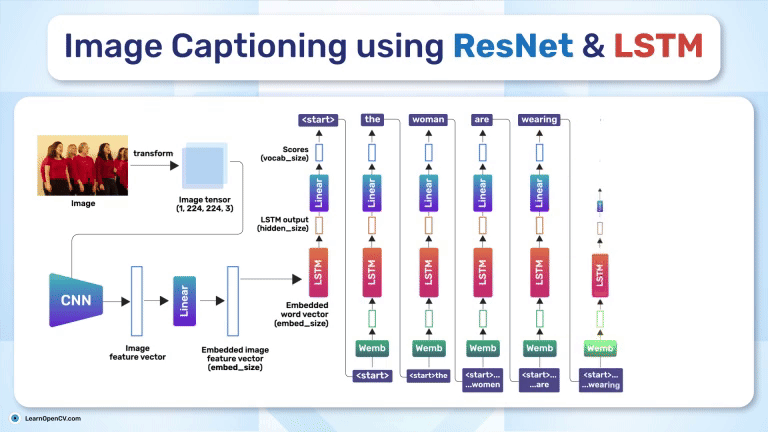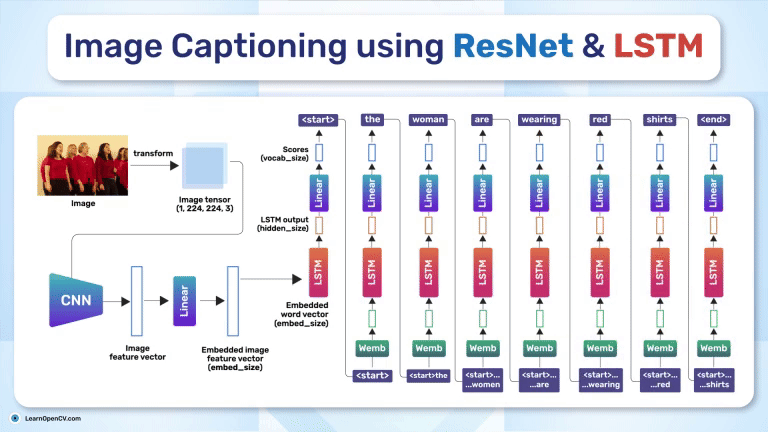
Search Results for: mac os – Page 5
Unsloth has emerged as a game-changer in the world of large language model (LLM) fine-tuning, addressing what has long been a resource-intensive and technically complex challenge. Adapting models like LLaMA,
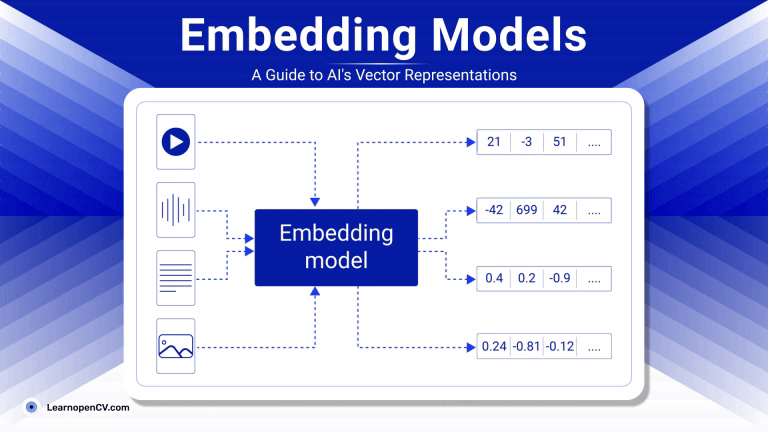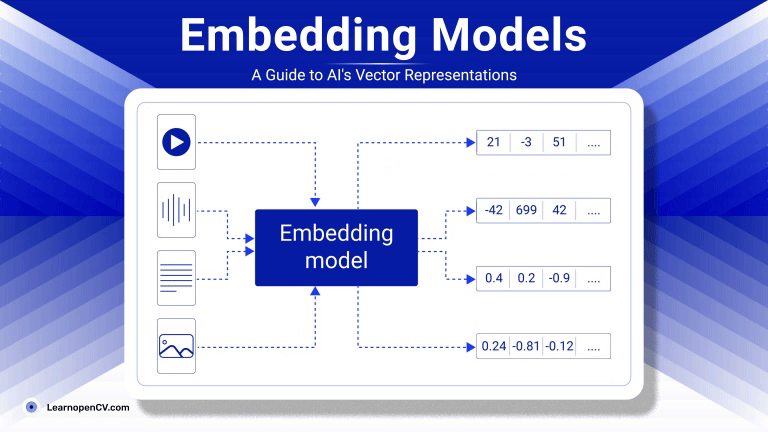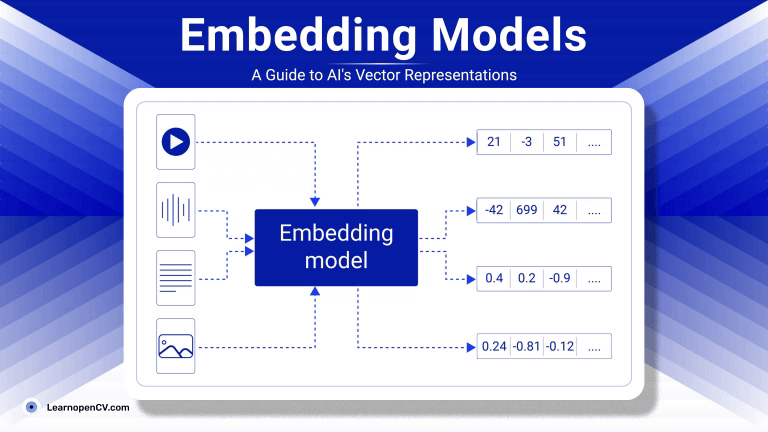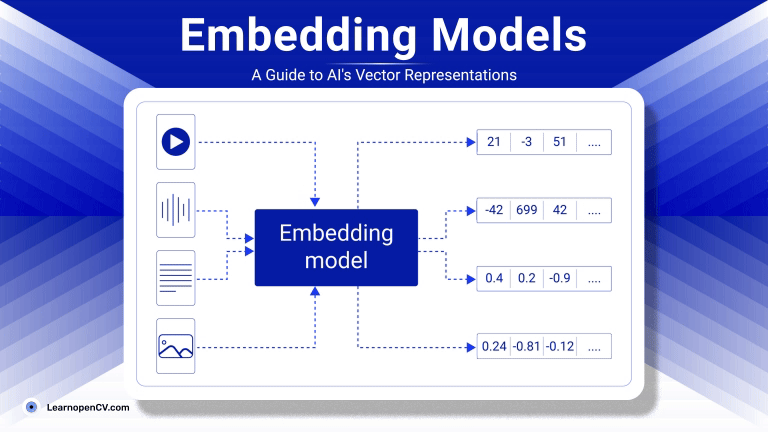
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, Embedding Models have become fundamental to how machines interpret and interact with unstructured data. By translating inputs like text, images, audio, and video into
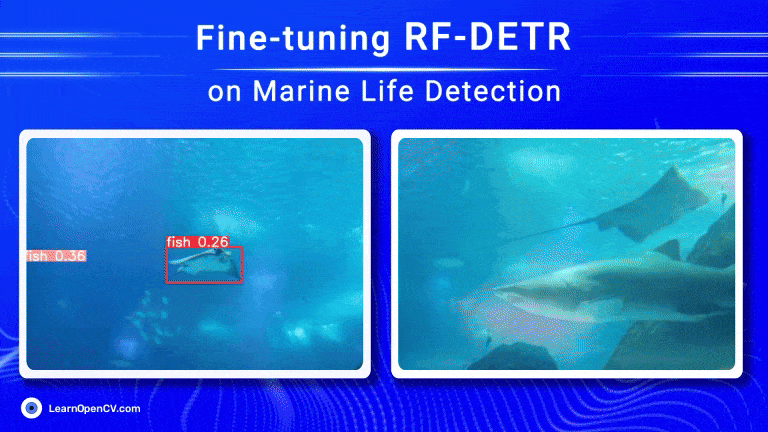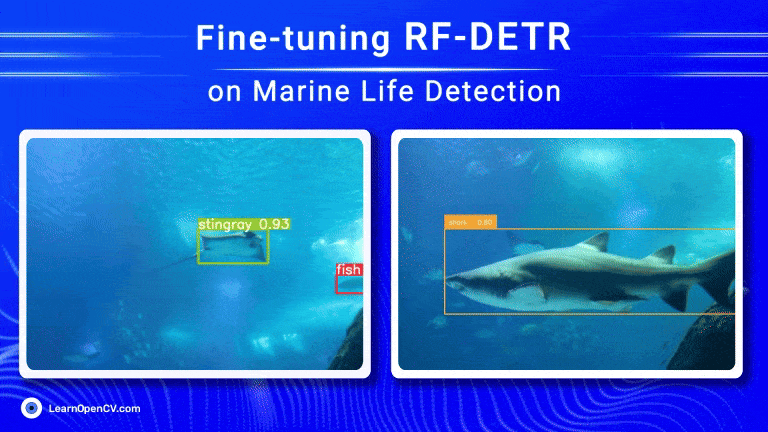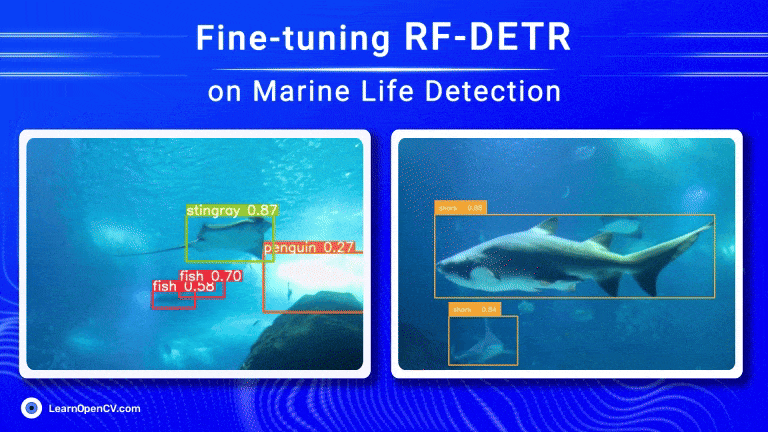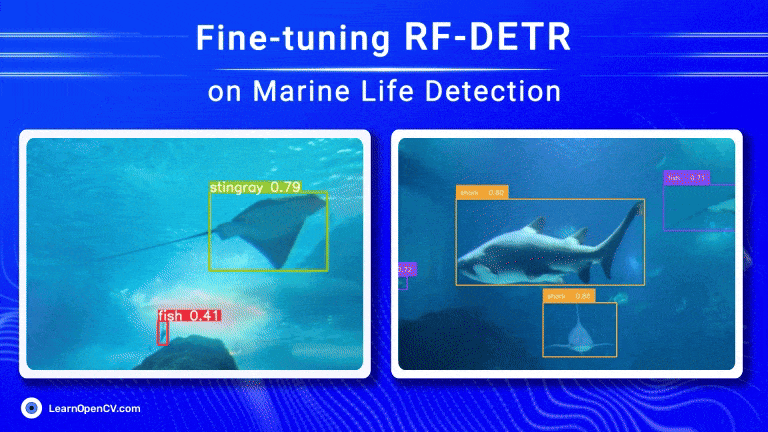
Object detection has come a long way, especially with the rise of transformer-based models. RF-DETR, developed by Roboflow, is one such model that offers both speed and accuracy. Using Roboflow’s
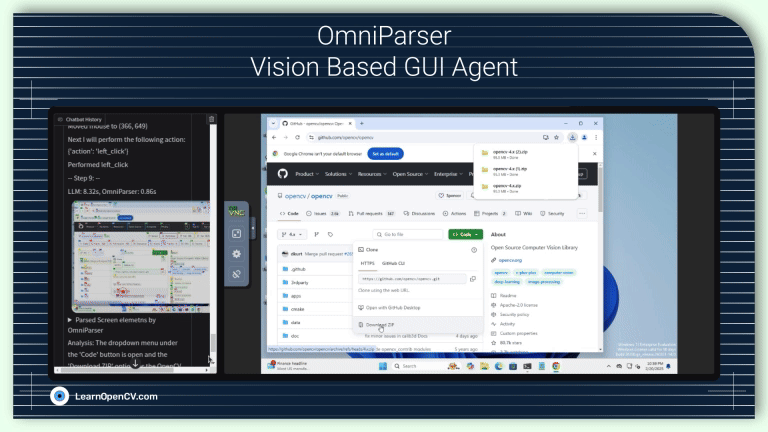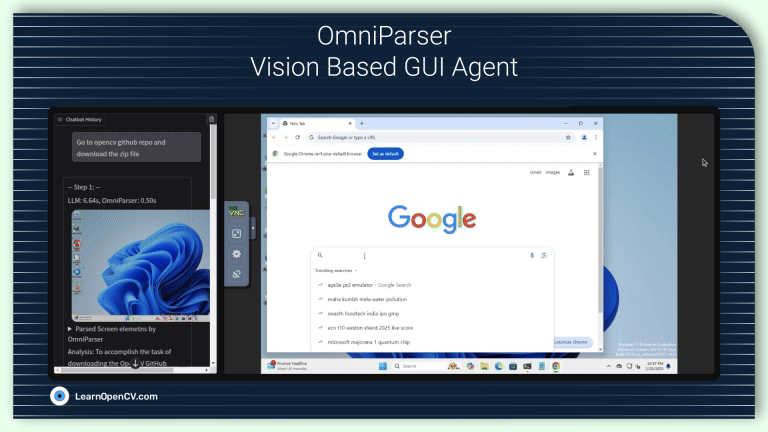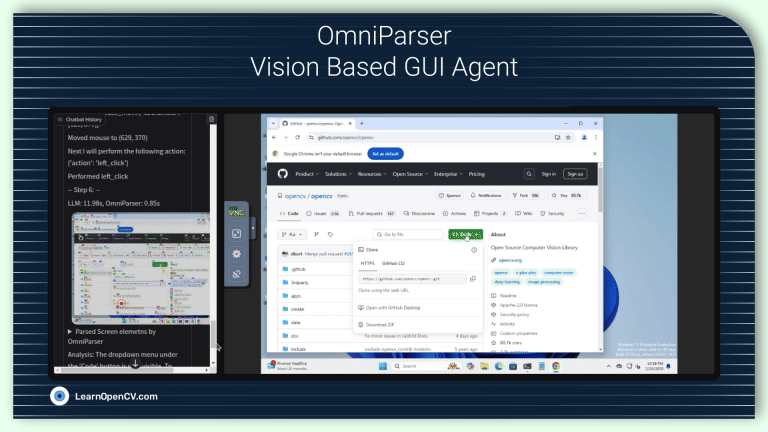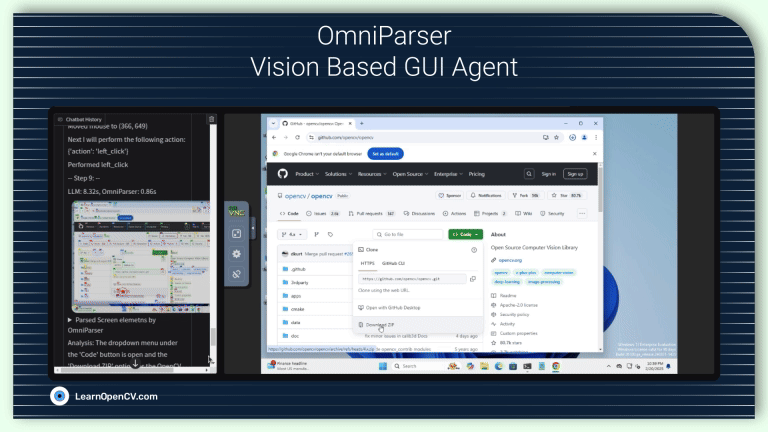
AI, being no longer confined to passive algorithms, is transforming itself into autonomous agents that can perceive, reason, and act with increasing intelligence. These agents are designed to navigate uncertainty,
3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has recently gained recognition as a groundbreaking approach in radiance fields and computer graphics. It stands out as a jack of all trades, addressing challenges that
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is redefining the landscape of 3D computer graphics and vision — but here’s a catch: it achieves groundbreaking results without relying on any neural networks, not