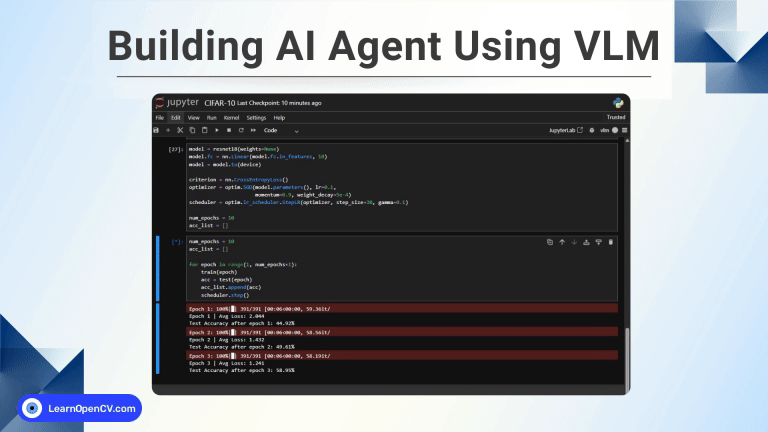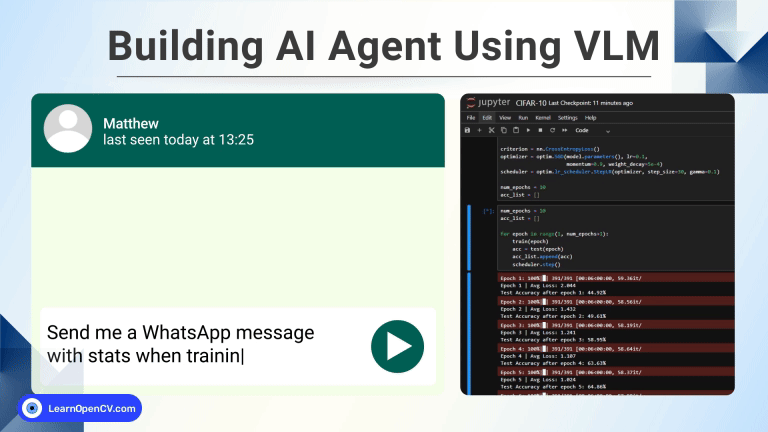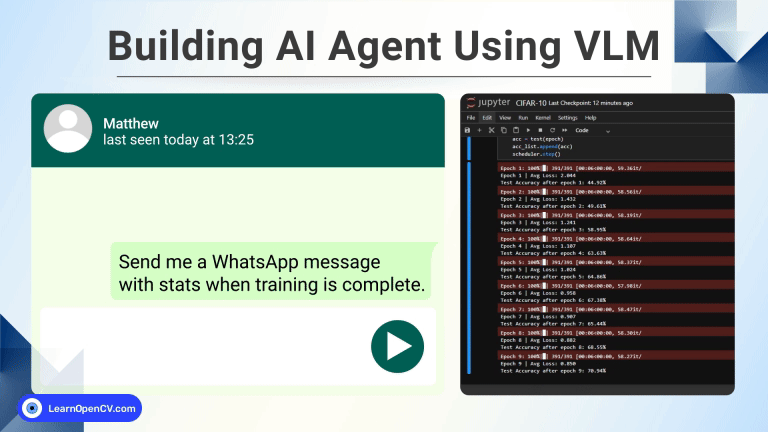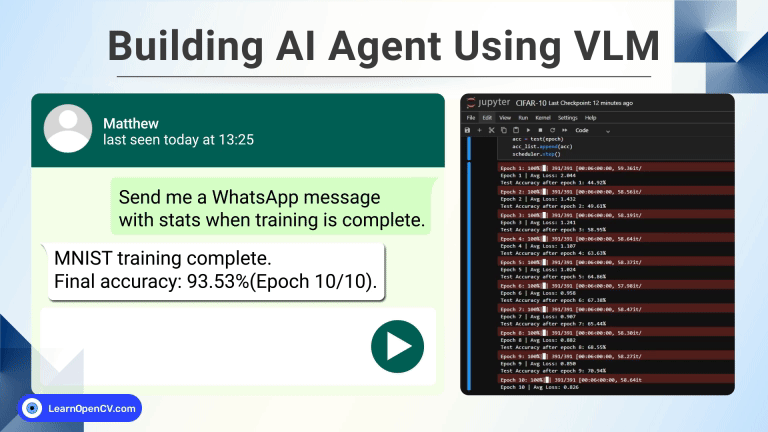
Large Language Models are increasingly moving from the cloud to the edge, driven by requirements for low latency, privacy, and cost-efficient deployment. While vLLM is widely regarded as the throughput leader on server-class GPUs, its behavior on resource-constrained, ARM-based edge devices is far less explored. In this article, we evaluate LLM deployment on the Jetson Orin Nano (8 GB) using vLLM, focusing on real deployment constraints such as memory pressure, concurrency, and stability. Using an in-house ChatML application, we compare vLLM against llama.cpp to understand where each framework fits in practical edge scenarios.
The goal is not synthetic benchmarking, but a deployment-first perspective on running production-style LLM services on an 8 GB edge device.
- 1. Introduction to SimpleChatUI
- 2. LLM on Edge Deployment Setup
- 3. Setup vLLM On Jetson Orin Nano
- 4. Start SimpleChatUI ChatML Application
- 5. Setting Up Web Search API as context for LLM
- 6. Build Llama.CPP on Jetson Orin Nano
- 7. Results of Deploying LLM on Edge through vLLM and Llama.CPP
- 8. Conclusion: Deploying LLM on Edge using vLLM and Llama.CPP
1. Introduction to SimpleChatUI
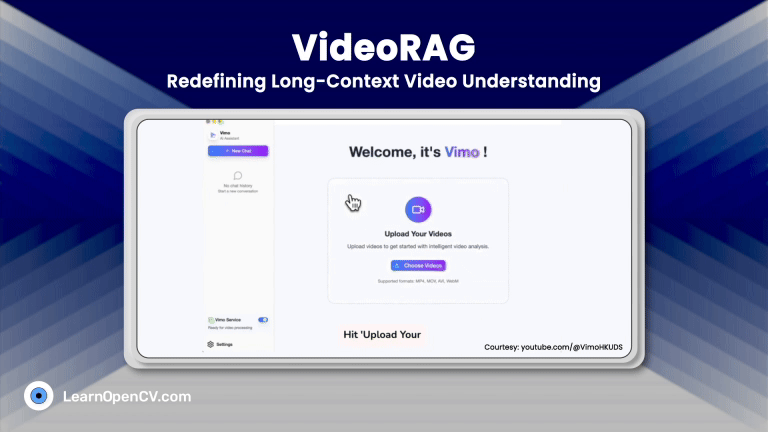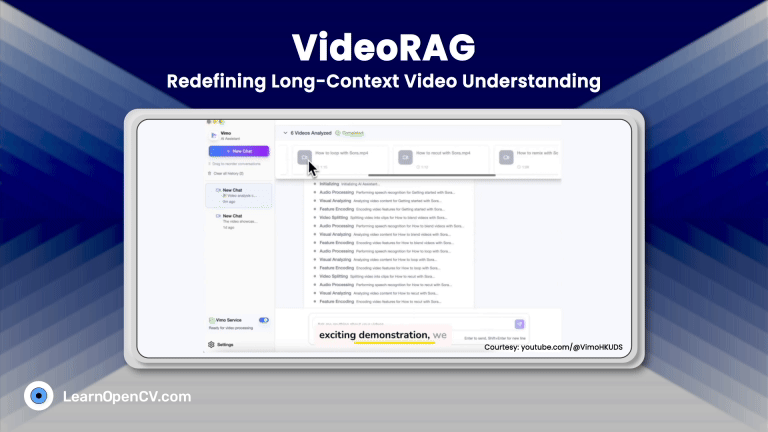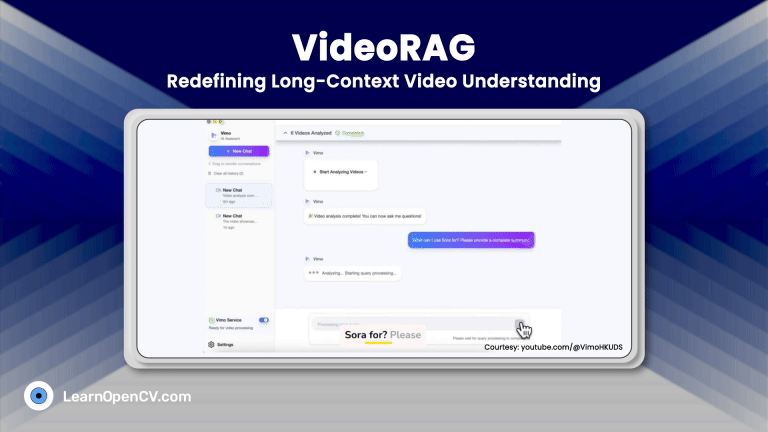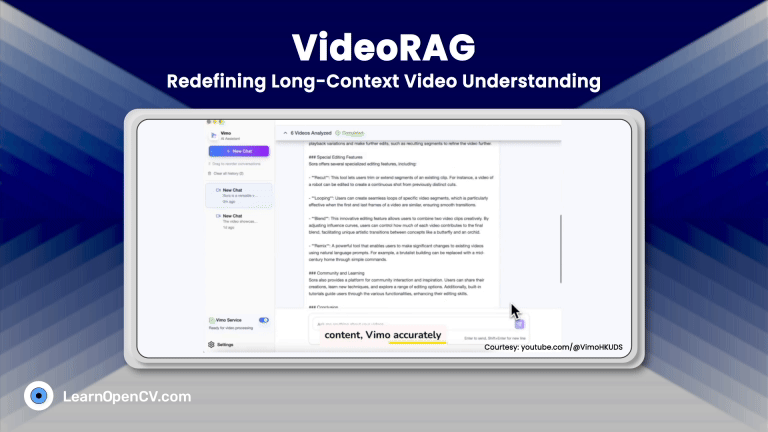
SimpleChatUI is a fullstack chatML application built for in-house local inference and experiments. It has both vision and language input processing feature. Integrated document processing with RAG, and Web search using Tavily. The chat history is maintained through in-memory vectorDB quadrant.
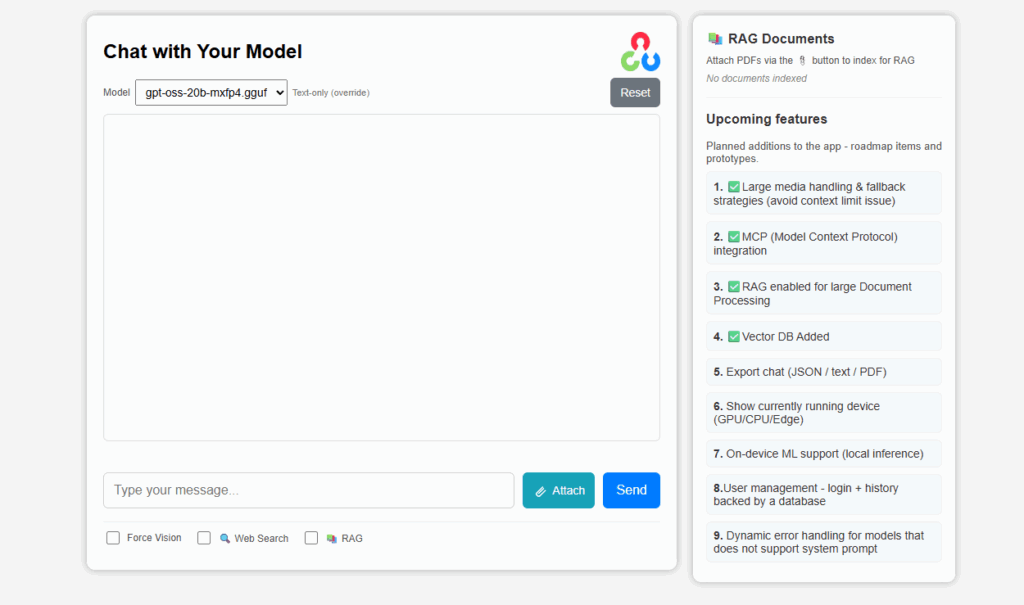
The entire application can be summarised to the following parts.
- A FastAPI backend managing files, requests, and in-memory database
- Responsive HTML-CSS frontend for chat
Install the requirements.txt file provided in the directory to sort out simpleChatUI dependencies, and proceed with next steps. You will find the downloadable code below or on the left menu bar.
2. LLM on Edge Deployment Setup
We are using the same edge cluster that we used for VLM on edge experiments earlier. Here, we are only using the Jetson Orin Nano, with 8GB memory, and 256 GB SSD. It is running Jetpack 6 and Cuda 12.6. Check out the Jetson setup video if you are doing it for the first time. For the inference server and chatML app, the system design is as follows.
3. Setup vLLM On Jetson Orin Nano
Although vLLM actively maintains the PyPi version, it did not work for me. The best way is to work with docker containers provided by Nvidia-AI-IoT. Just pull the container, and you are ready to serve models using vLLM.
docker pull ghcr.io/nvidia-ai-iot/vllm:latest-jetson-orin
It will take some time depending on the internet speed. Once container is pulled, run it using the following command.
3.1 Run vLLM Container
docker run --rm -it --runtime nvidia \
--gpus all --network host --shm-size=8g \
-v $HOME/.cache/huggingface:/root/.cache/huggingface \
-v $PWD:/workspace \
ghcr.io/nvidia-ai-iot/vllm:latest-jetson-orin
The flags used and their meaning are as follows.
--runtime nvidiaand--gpus all: Enable CUDA and expose the board’s GPU inside the container. With this framweworks like vLLM, or llama.cpp can use hardware acceleration.--network host: Container shares the host’s network stack, makinglocalhostinside the container identical to the host--shm-size=8g: Increases shared memory to 8 GB, preventing crashes or slowdowns common in ML workloads.$HOME/.cache/huggingface: The volume mount allows downloaded models to persist across container runs
3.2 Start vLLM Engine for Serving LLM on Edge
We are using LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Instructmodel for our experiment here. The model will be loaded as it is with half precision – BF16. The serving command is as follows.
vllm serve LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.5 \
--max-model-len 4096 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 1024 \
The command downloads the model from huggingface (if not already done), and starts vllm engine. This setting allows me approx 17 concurrent users, and 40 token/sec throughput. Try increasing the model length, batched tokens, and gpu memory utilization.
The server starts a OpenAI-compatible v1 endpoint at port 8000 by deafult. You can change the port to something else using --portflag. However, make sure to change the port in below applications as well.
Find basic details of deployment engine vLLM here.
3.3 Handling Fail Cases while Deploying LLMs on Jetson
Unable to get server running? Don’t worry, you are not the first. The biggest problem of the Jetson Orin Nano is that 8GB unified memory is too less. All of the system processes are running within this constrained space. There are a few memory optimization techniques, mentioned in official Nvidia Jetson site. You may have to close down few unnecessary services.
Secondly, the issue of memory fragmentation. You can’t really do anything about it. It’s bound to happen over time. Method that helps are as follows:
- Clear cache using jtop utility once in a while
- Shutdown and perform cold boot
If still not working, showing OOM, or not enough contiguous blocks. Try enforcing eager backend. This will also disable CUDA graphs. The number of concurrency is reduced to 1. As you can see, I have also reduced GPU utilization limit.
vllm serve LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.4 \
--max-model-len 4096 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 1024 \
--max-num-seq 1 \
--enforce-eager
After going through the above steps, try again. It should work fine now. If it worked at the very first time, it’s fine – now you know what to do when it fails.
4. Start SimpleChatUI ChatML Application
The reason for using only 40% of GPU above is becuase we have to run few other things. The chatML app backend, and something like ngrok or cloudflared tunnel to expose it.
Navigate to the downloaded code directory, and install the requirements.txt file. On a separate terminal session, we will run the following.
export OPENAI_API_BASE=http://0.0.0.0:8000/v1
uvicorn app.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 3000
This will run the application in port http://0.0.0.0:3000. Now, to make the application accessible to anywhere in the world, we will use cloudflared tunnel. Installation commands are as follows. Successful running will return an public URL, something like – https://jellybean-mango-bite.trycloudflare.com.
curl -L https://github.com/cloudflare/cloudflared/releases/latest/download/cloudflared-linux-arm64 \
-o cloudflared
chmod +x cloudflared
sudo mv cloudflared /usr/local/bin/
# Confirm version with
cloudflared --version
# Run cloudflared tunnel
cloudflared tunnel --url http://0.0.0.0:3000
The server will stay alive for some time depending on the following. No gurantee of uptime with temporary domains. You can configure personal domains if you have one for persistent link.
- Jetson in running
- Terminal not closed
- Network fluctuations
- Idle – no requests for long time, cloudflared may reclaim the same
5. Setting Up Web Search API as context for LLM
simpleChatUI is also integrated with websearch as context for the LLM chat. We are using Tavily for the same. For this however, you need a tavily account. It allows 1000 free credits for experiments (as of Jan, 2026).
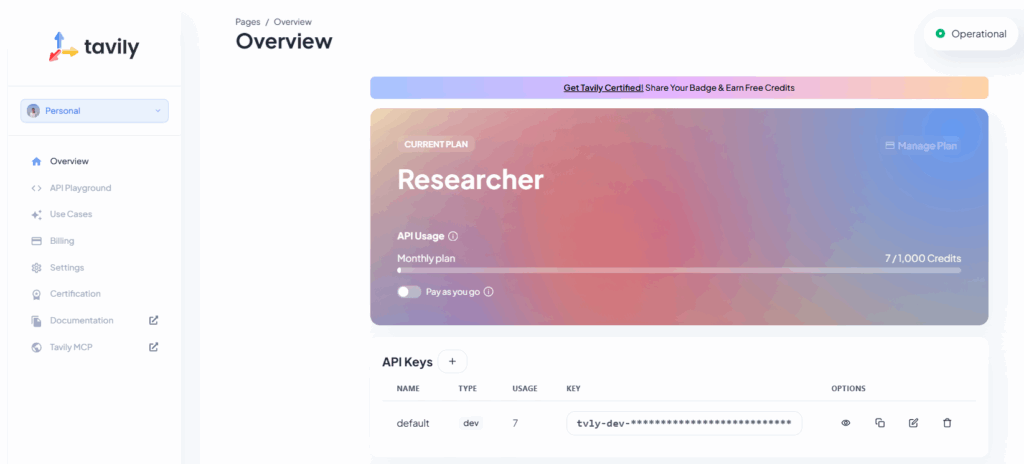
The default API key can be used directly, or refresh a new one specifically for the test case. If the chatML application server is running, close it first. Then run the following command. Make sure to sue the same terminal session. Then run the uvicorn command again.
export TAVILY_API_KEY={add-your-api-key-here-without-curly-braces}
With the web search enabled, play with the chat for some more time. Observe the output quality, and speed. See if it is able to meet your expectations. Next, we will setup llama.cppserver.
6. Build Llama.CPP on Jetson Orin Nano
Llama.cpp is built for efficiency, targeting on-device inference. However, it still takes advantage of GPU backend (if available). To make the comparison fair, we will build with CUDA flag ON. Execute the commands as follows.
Ps: Turn off vLLM server now (if you are working on this step). Building is process intensive as well. No need to turn off cloudflared tunnel and fastapi server.
6.1 Install Dependencies for Llama.CPP Build
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y \
git cmake build-essential \
python3 python3-pip \
libopenblas-dev \
libcurl4-openssl-dev
6.2 Clone Repositories and Start Build
git clone https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp.git
cd llama.cpp && mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DGGML_CUDA=ON -DCMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES=87 -DGGML_OPENBLAS=ON
cmake --build . -j$(nproc)
If the build is crashing, or stuck – reduce the core nproc=4 . Upon successfull building, you will observe llama-cli, llama-server, llama-bench and many more binaries in llama.cpp/build/bin directory.
6.3 Start Llama.CPP Server on Jetson Orin Nano
With the binaries built, navigate to llama.cpp/build/bin/ directory and run the following command. We are using the BF16 model, with same model length, for fair comparison. The default port is 8080 for llama.cpp, hence we are using 8000 explicitly.
llama-server -hf LiquidAI/LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct-GGUF:BF16 \
--port 8000 \
--ctx-size 4096
Reload the chatML application and continue chatting as usual.
7. Results of Deploying LLM on Edge through vLLM and Llama.CPP
For a resource constarined device like Jetson Orin Nano, the results are impressive. It was serving peak throughput of 40 token/sec in some cases. Check the table below for comparison.
7.1. Throughput Comparsion
| Prompt | Llama.CPP (token/sec) | vLLM (token/sec) |
|---|---|---|
| Hi (First Prompt) | ~1 | ~2 |
| Write an essay on cow | 35 | ~40 |
| Explain YOLOv4 vs YOLOv5 | 26 | 26 |
| Write python code – perform object detection using Ultralytics YOLOv8 medium model. Use OpenCV and related libs to perform the same. | 24 | 26 |
Although I expected significantly higher throughput from vLLM, it didn’t happen. It is slightly faster but not by a huge margin.
7.2 Memory Utilization and Concurrency
vLLM consumes significantly high memory 6.4 GB compared to 4.2 GB by llama.cpp server. Concurrency was vLLM is unbeatable.
| Particulars | Llama.CPP | vLLM |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Utilization | 4.2 GB | 6.4GB |
| Max Concurrent Users | 4 Nos | 17 Nos |
8. Conclusion: Deploying LLM on Edge using vLLM and Llama.CPP
This experiment demonstrates that running production-grade LLM servers on edge devices like Jetson Orin Nano is not only feasible, but practical. Given that expectations are set correctly. Both vLLM and llama.cpp delivered usable throughput, stable responses, and acceptable latency despite the obvious constraints.
From the results, a clear trade-off emerges. llama.cpp excels in memory efficiency, making it a safer choice for single-user or low-concurrency scenarios where system stability is critical. On the other hand, vLLM’s strength lies in concurrency, enabling significantly more simultaneous users.
Interestingly, the performance gap between the two frameworks narrows considerably on ARM-based edge GPUs. This highlights an important insight: on constrained devices, memory bandwidth, fragmentation, and system overhead often dominate over algorithmic optimizations that shine on larger GPUs. In such environments, deployment strategy matters as much as the inference engine itself.
For edge practitioners, the choice is straightforward:
- Use llama.cpp when memory headroom is tight and user concurrency is low.
- Use vLLM when serving multiple clients, integrating RAG, or exposing LLMs as shared services, even on small devices.
As Jetson platforms evolve and techniques like quantization, speculative decoding, and KV-cache optimizations mature, the boundary between “edge” and “server-grade” LLM deployment will continue to blur. This experiment is a strong indication that edge AI is no longer limited to inference demos, it is ready for real applications.
With this we wrap up the blog post on deploying LLMs on Edge using vLLM and Llama.CPP. I hope you enjoyed reading the article. Please feel free to comment below for next blog post ideas, bugs, or any general suggestios if any. Happy Learning!
Yes, vLLM can run reliably on Jetson Orin Nano, but careful memory tuning is essential. With default settings, vLLM may fail due to out-of-memory errors or memory fragmentation. Limiting GPU memory utilization, reducing the maximum number of batched tokens, and lowering concurrency are often required. In constrained scenarios, enabling eager execution can help stabilize the server at the cost of reduced parallelism. With proper tuning, vLLM is stable and usable for real applications.
Choose llama.cpp when memory efficiency and simplicity are your top priorities. It consumes significantly less memory and is better suited for single-user or low-concurrency workloads on edge devices. In contrast, vLLM is the better choice when you need higher concurrency, OpenAI-compatible APIs, or integration with RAG and web-based applications. On Jetson-class hardware, the performance gap in raw throughput is small, so the decision is largely driven by memory headroom and concurrency requirements.
The primary bottleneck is unified memory, not raw GPU compute. All system processes, the OS, and the model share the same memory pool, making fragmentation and allocation failures common. Secondary factors include limited memory bandwidth, CUDA graph constraints, and background services consuming GPU or RAM. Effective edge deployment depends more on memory management and system tuning than on model architecture alone.